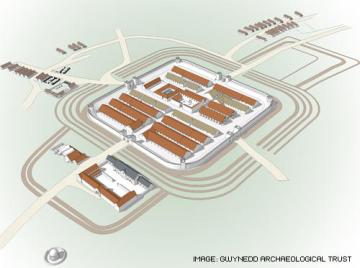
Simplified reconstruction of Pennal Fort by Gwynedd Archaeological Trust: Source: Gwynedd Archaeological Trust
The nearest Roman site to Aberdovey is the fort at Pennal, called Cefn-Caer (which translates roughly as ridge/hillside of the fort), 10.5km (6.7miles) away from Aberdovey. Although there is a rock-cut track that stretches from Penhelig to Picnic Island along the estuary that is known locally as the Roman Road, this actually dates to 1827. Cefn Caer at Pennal, however, is the real thing: a Roman fort 600 yards from Pennal down a small B-road. It formed part of a network of forts and roads that were key to the Roman plans to subjugate Wales. When I first started looking into Cefn Caer for this post, it was simply because the site is part of this area’s history and I wanted to include it as a small representatives of Roman activity in Wales. The word “small” is worth noting here, because I was expecting Cefn Caer to be no more than a very ephemeral way station for travellers (mansio) or a tiny watch-post. In fact, it is a fairly substantial affair, as demonstrated by the above simplified reconstruction by Gwynedd Archaeological Trust (GAT). The GAT work at the site reveals an auxiliary fort with all the features associated with a permanent installation, which had an important strategic role.

Pre-Roman Wales. Source: Wikipedia
The Roman Empire first made its presence felt on British shores first under no less a personage than the Emperor Julius Caesar, albeit only briefly in 55BC and 54BC. Under the Emperor Claudius matters were taken far more seriously in AD 43 and there was to be no retreat, and after the invasion most of Britain was incorporated in the Roman Empire for for the best part of 400 years. The period of the Roman occupation of Britain is known as the Romano-British period (AD 43 to 410).
Iron Age Britain immediately prior to the invasion was divided into six main tribal areas, recorded in Roman documents, which were organized in social hierarchies that were based on lineage, status and military aptitude “cemented by the distribution of favours and hospitality; consequently equipment for eating looms large in the archaeological record” (Davies and Lynch 2000). Parade gear, with a particular focus on horses and chariots, is also dominant in the archaeological record. Subsistence practices depended very much upon geography, but combined herding of domesticated animals (cattle, sheep, goat and pigs) with the cultivation, where possible, of emmer wheat and barley. Hillforts are generally thought of as synonymous with the Iron Age, as places where political power was centred, but in mid-west Wales, where there are very few hillforts, suggesting that political power was more fragmented, and consisted of scattered farmsteads. Although the Tal y Llyn hoard (covered on an earlier post) found at Cader Idris is very rich, it is entirely possible that it was hidden by someone travelling through the area, rather than a local resident. Although in some areas life went on without disruption for some time, in the areas where the invaders first settled, they introduced substantial change very quickly.
When Aulus Plautius, the chosen commander of the Emperor Claudius, led an invasion force to Britain and landed in the southeast, he found the prosperous and sophisticated Catuvellauni tribe dominant, their territory extending from Essex to Surrey under the leadership of Caratacus and his brother Togodummus. Caratacus and Togodummus were defeated when confronted with the 40,000 men in four legions and supporting auxiliary forces. Caratacus abandoned his family and fled to the Silures tribe in southeast Wales to rethink his strategy. Caratacus realized that the partially low-lying territory of the Silures was vulnerable and created an alliance with the Ordovices, which had highland areas in its territory, to organize resistanc,. The Ordovices were the main tribe occupying most of Gwynedd and Ceredigion, and “by creating a multi-tribe resistance he [Caratacus] offered the most effective bulwark against the Roman invasion to date” (de la Bédoyère 2003).

Cefn Caer, showing farm buildings with traces of the Roman fort in the field to its right. Source: RCAHMW (on the Coflein website) Catalogue Number C872327, File Reference : AP_2009_1671. By Toby Driver
It was not until AD 47 that the Romans felt the need to turn their attention to the tribal areas of what is now known as Wales. Wales had many benefits from a Roman point of view, including rich mineral resources, fertile valleys and a long coastline. It would also have been a good source of manpower via voluntary enlistment or conscription. Perhaps most important, strategically, without peace in rebellious Wales, all Roman-controlled land to its east was potentially under threat. The first period of military hostilities between Rome and Wales lasted between AD 47 and AD 60, with multiple campaigns against the Marches and Welsh communities, starting in the southeast. A significant event was the Battle of Caer Caradoc in AD 50, where Caratacus led armies composed of the Ordovices and Silures against the Roman military. In spite of the strategic advantage of Caratacus and his armies, holding the high ground, the Roman forces under the governor Publius Ostorius Scapula had weaponry, body armour and military experience that outclassed Silurian and Ordovician resources. Caratacus was defeated and ultimately taken into custody and carried to Rome where the Roman senate were sufficiently impressed by his speech that he earned a pardon from Claudius and lived out his life in Rome. In his book “Defying Rome,” de la Bédoyère comments that Caratacus “failed to appreciate that he was on the whole a dinosaur. While he maintained his resistance he found the only place he could do so was amongst people who had no idea what Rome amounted to.” The Romans did not have it all their own way, but although the Silures went on to defeat a Roman legion in AD 52, it was only a matter of time before Wales was brought under Roman control. There was a brief respite when the Boudiccan rebellion in East Anglia in AD 60 required the redeployment of troops. Full-scale invasion was temporarily abandoned and a strategy of containment was practised in Wales, with all of the only permanently occupied military bases lying along the border.

Wroxeter (Viroconium Cornoviorum). Source: Wikpedia. Photograph by Alastair Rae
In AD 73 under the Emperor Vespasian, Sextus Julius Frontinus was appointed Governor of Britain (AD 73-77) , and it is during his tenure that Wales was fully conquered. Three legionary fortresses were established as campaign bases, at Caerleon (Isca Silurum), Wroxeter (Viroconium Cornoviorum) and Chester (Deva Victrix), and temporary camps were set up within Wales itself, setting the scene for “a network of garrison posts, incorporating fortlets and watchtowers, eventually linked by an all-weather road system” (Arnold and Davies) which were used to maintain control over the rural and often highland zones.
Information about Iron Age and Romano-British exploitation of the western areas of west of mid Wales is particularly sparse, but it would be surprising if such rich natural resources as the Dyfi and particularly Dysynni valleys were not employed for cattle herding and some cultivation, with the surrounding highlands excellent for sheep herding. It is by no means clear if the Ordovices occupied the whole area, as the boundaries of tribal areas are not known, and it is thought that other smaller and less dominant communities also occupied parts of Wales, but it seems clear that whatever happened to the Ordovices would have had an impact on other small communities in the area. After their defeat under the leadership of Caratacus in AD 50, the Ordovician tribe again rebelled in AD 77-78 and was put down uncompromisingly by the British governor, Gnaeus Julius Agricola. Agricola went on to establish forts at Caernarfon, Caersws, Pen Llystyn (Bryncir), Tomen y Mur (Trawsfynydd), Caer Gai (Penllyn) and Cefn Caer (Pennal), most of them in river valleys or estuaries. Other sites in the mid Wales area established in this period were the fortlets at Erglodd in Ceredigion and Brithdir in Merionnydd.
The Roman architectural infrastructure in Wales took the same form as it did elsewhere, a hierarchy of military installations. The most important in strategic, organizational and to an extent administrative terms were the legionary fortresses at Chester (Deva), Wroxeter (Viroconium Cornoviorum) and Caerleon (Isca Silurum). These were, however, in a minority, and the main control over Wales was exercised by a large number of auxiliary forts dotted at strategic positions throughout Wales, often on rivers and estuaries, supplemented at intervals by small fortlets and watch towers. Legionary and auxiliary forts each refer to the type of garrison stationed there. Legions were the elite army of the Roman Empire, composed of c.5000 men, divided into ten cohorts. They served for twenty-five years and were rewarded on retirement with a choice of land or a payment. Auxiliaries were composed of non-Roman citizens, men who entered the army from throughout the Roman empire sometimes sometimes as volunteers but sometimes extracted from their homes by force. They were granted Roman citizenship once they retired. They were far more numerous than the legionary forces and were essential to the Roman occupation of Britain. Mid Wales in the Romano-British period remains poorly understood, which means that wherever a Roman site or a contemporary Iron Age is identified in the area, it is potentially of considerable importance for understanding what was happening in mid Wales at this time. The Cefn Caer fort was an auxiliary fort, the westernmost of Roman structures in Meirionnydd, established in the AD 70s.
There are few visible features of Cefn Caer on the ground. The ramparts to the southwest and northwest can be made out, but elsewhere they are low banks that cannot always be seen. Before it was torn down and rebuilt in 1769 the church in the village of Pennal was reported to include a large number of Roman brick in its walls, and remaining obstructions to cultivation were probably moved in the distant past, and the land continues to be used by the local farm for cultivation. The farm buildings, including a sub-Medieval farmhouse (which can be visited), sit within the west corner of the fort and the northern corner of the fort is crossed by a small B-road Although the 1967 History of Merioneth provided dimensions derived from previous surveys of the fort, detailed knowledge of the scale and structure of the fort comes from more recent analysis of aerial photographs, the use of geophysical survey and field excavations, the latter only sampling certain parts of the site. The history of the archaeological work can be summarized as follows. The site was first noted by Robert Vaughan in his Survey of Merioneth in the mid 17th Century, and in a late 17th Century letter by the rector of Dolgellau, Maurice Jones. Amongst the 17th Century finds were a silver coin inscribed with the name of the Emperor Domition. Subsequent visits to the site reported ditches, coins, bricks, a hard paved road, pottery and a tile relating to II Augustian Legion. The main sources of information are the initial detailed report by Professor R. C. Bosanquet in 1921, which was further studied and commented upon in 1957 by H.C. Irvine in BBCS Volume XVII part 2, and these were the best sources of information on the subject prior to the work by Gwynedd Archaeological Trust (GAT). GAT used conventional survey, geophysical survey, and excavated some sample trenches to investigate further (Hopewell 2001, 2003).
Cefn Caer was a small auxiliary fort (castellum) with traces of a ditch still visible at the northwest, outside the rectangular bank that encloses the fort. It was built in AD 70s. It is more than 1.68ha (5 acres) in area, measuring 140m x 120m (c.550ft x 425ft) northeast to southwest with rounded corners. An earlier site of c.2.4ha appears to have predated it, which may have been the temporary fort established before the construction of the permanent site. The fort was located at the west end of a ridge or spur that rises 15m (50ft) above the floodplain north of the river Dyfi, c.10km (c. 6 miles) from the mouth of the estuary. This offered it the dual benefits of having something of a view over the surrounding area, and in particular the river crossing. It was only 100m (328ft) northeast of the marshy Dyfi floodplain and 1.6km (half a mile) from the river itself, where “tongues of the land extend opposite each other to both banks of the river” (History of Merioneth) providing an ideal place for fording the river, and where coastal vessels could unload. Roman forts were built to a fairly standardized template, meaning that they could be built rapidly without resorting to labour beyond the personnel they had to hand, and Cefn Caer does not deviate from this basic form. For comprehensive details see Hopewell 2003 (available to download – link also at the end of this post) but here are some of the key features that Hopewell describes, with numbers in the text referring to the site plan, copied here.
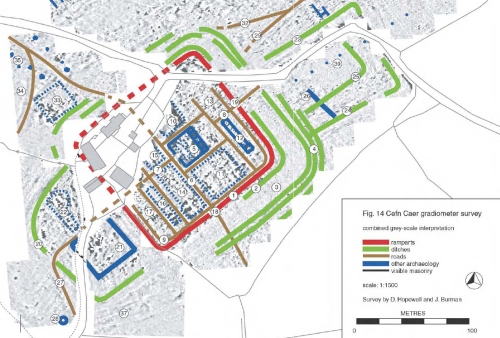
Resuilts of the GAT geophsyical survey at Cefn Caer. Source: Hopewell 2003, Gwynedd Archaeological Trust
Cefn Caer was arranged around two main axes that crossed the fort at right-angles to each other, one on a northeast to southwest axis, the other crossing it on a northwest to southeast axis, and the whole fort was surrounded by defensive ditches. At its centre, on a natural rise, were the fort’s stone-founded headquarters, the principia (principal buildings – no.5 on the above plan) measuring 25m x 28m. Several other buildings also appear to have had stone foundations. The entrance to the principia is on the south-west side, and “leads into a courtyard with a portico on four sides bounded by a cross hall at the rear. At the rear of the building stand a set of five rooms comprising a central shrine room (sacellum) with offices to either side” (Hopewell 2003). There are two buildings either side of the via principia. GAT interprets the building to the north-west (10) as the praetorium (commander’s house). In the retentura (rear part of the fort) one block of centuriae (military barracks) (12 on the above plan) can clearly be seen. The officer’s quarters stand towards the corner of the fort. Part of the space in the praetentura (the front part of the fort) appears to be taken up by two ranges of centuriae. Part of the big building complex (14) may be a stable block with the stalls. Within the fort are a number of roads, which are standard for an auxiliary fort, as follows:
- The via principalis (6 on the above plan), running from north-west to the south-east across the centre of the fort.
- A short length of the via praetoria (7) runs at right angles to the via principalis under the farmyard
- The via decumana (8) runs from the rear of the principia to the north-eastern gate
- The via sagularis (9) runs around the inside of the ramparts
Beyond the main limits of the fort a vicus developed to the northeast and northwest. A vicus is a small settlement associated with an auxiliary fort, a community of traders and their families, who supplied good to the garrisons within, but its inhabitants were rarely local, and were just as much outsiders as those within the fort. Marriage was forbidden to Roman soldiers, but there is little doubt that less formal arrangements existed, and that families of soldiers also resided within the vicus. The presence of a vicus next to the fort is indicative of its permanence and relative longevity. Below the southwestern annex there was a small circular building that was probably a small temple, shrine or tomb. A large rectangular building (33 on the above plan) measuring 34 x 22m may be a mansio (travellers’ way station). A mid 19th Century visit by the Cambrian Archaeological Association mentions the remains of a hypocaust (sub-floor heating, sometimes associated with bath complexes), and this appears to have been located in an annex to the northwest of the fort (22) where there is plenty of Roman tile on the surface.
The fort has four entrances, one in the centre of each side, and there have been some efforts to determine where the roads that terminated here linked to locally. A small B-road cuts across the north corner of the site, shown in the plan from History of Merioneth to the left, and the History of Merioneth suggests that the sudden kink in the road indicates that for a short span it follows the Roman road that emerged from the site. Evidence of the same Roman road a little further on appears to run along a nearby ridge. There was also an earlier indication that portions of a road led from the southwest gate led down to the river. The History of Merioneth suggests that this may have led to a quay at Llyn y Bwtri. The southeast gate would have faced the river crossing. Cefn Caer appears to be linked to a number of national routes as follows.
- Via the fortlet at Brithdir towards Tomen y mur (to the northeast of Llyn Trawsfynydd. Tomen y Mur is considered to have been the most important Gwynedd fort due to its strategic position, its size and its complex layout, with an amphitheatre, bath house, vicus, mansio and related structures, including a possible aqueduct. Although the roads connecting it are not completely mapped, it is clear that it was an important link between mid (and south) Wales with the important sites of Caernarfon and Canovium (Caerbun) to the north, which were in turn connected to the regional capital at Chester.
- Via the fortlet at Brithdir northeast towards the important fort of Chester), via smaller forts at Caer Gai and Llanfor.
- Cefn Caer probably linked to another route, this time west to another ciwitas captial at Wroxeter via the fortlet at Pen y Crogbren and the forts at Caersws and Forden Gaer.
- It was also clearly connected with sites to the south of the river Dyfi, in the first instance the fortlet at Erglodd and, in turn, the forts at Pen Llwyn and Cae Gaer. These were on routes to the important southern Welsh fort Caerleon.
These are all shown on the map of Roman Wales above and although the road network cannot currently be completed, the map indicates how Pennal was linked to other sites in the area, providing an important intersection at the river Dyfi between north and south parts of west Wales.

Brithdir fortlet from the air. Source: RCAHMW colour oblique photograph of Brithdir Roman fortlet. Taken by Toby Driver on 11/12/2007. Published on the Coflein website.
Another Meirionnydd fort at Brithdir, 3 miles east of Dolgellau, was found in the early 1960s and is clearly connected by a contemporary road to Cefn Caer at Pennal. It measured c.184x184ft (54m sq), so was much smaller than the Cefn Caer fort. It has not been excavated and there are no extant remains, but it shows up very clearly in aerial photographs like the one at left, and in the early 1990s geophysical survey was carried out at the fortlet. When a new housing estate was under construction nearby in the 1970s the opportunity was taken to excavate, and the results of these combined sources show a complex history at and around the site. At least two and possibly three, ditches surrounded the fort, and there are indications that a bathhouse and workshops were present. Brithdir was considered to have been built to guard an important intersection of a number of routes.

The fortlet at Erglodd in Ceredigion. Source: Gwynedd Archaeological Trust
Looking to the south of Cefn Caer, the nearest site on the other side of the river was the fortlet at Erglodd, to which it was presumably connected by a road to the Dyfi ford. You can read more about the results of the geophysical survey in the Gwynedd Archaeological Report on the subject (Hopewell 2007).
Unlike the other parts of England and Wales, there is no evidence for towns developing or villas being built in Mid Wales. Arnold and Davies say that this “may be a silent commentary not just upon native resistance but upon the inability of the agrarian base to produce the necessary surplus. Together with geographical constraints, this inhibited political co-operation and fostered continuation of highly segmented societies.”
In the period AD 78-83, again in AD 98-119 and then again in AD 125-6 troops were required in the north of Britain (eventually resulting in Hadrian’s Wall and Antonine Wall) and overseas, when some troops were again withdrawn from Wales. Some forts were abandoned whilst others, like Tomen-y-Mur at Trawsfynydd, were resized and operated with less manpower. By AD 140 very few auxiliary forts were occupied in Wales and it is probable that Cefn Caer was abandoned either at this stage, or during the 3rd Century, when most of Wales was abandoned.
A lot of unanswered questions may be tackled in the future. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust’s Roman Fort Environs Project funded by Cadw is researching the environs of a number of forts using fluxgate gradiometer survey, which should help to develop an understanding not only of the forts but of their ancillary structures, roads and supporting settlements. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust has so far carried out surveys at Canovium (Caerhun), Caer Gai (Llanuwchllyn), Caer Llugwy (Capel Curig), Cefn Caer (Pennal) and Pen Llystyn (Bryncir). These findings will be published in the future. At the same time, a number of GAT and independent projects are looking for the remains of Roman roads in areas where the linkages are known only from small sections, in order to fill the gaps in knowledge about the roads between forts and the routes they followed. Research by Hugh Toller, for example, is thought to have uncovered a number of previously unknown sections of the RRX96 road between Pennal and Brithdir.
Main sources:
Arnold, C.J. and Davies, J.L. 2002. Roman and Early Medieval Wales. Sutton Publishing
de la Bedoyere, G. 2003. Defying Rome. The Rebels of Roman Britain. Tempus
Bosanquet, R.C. 1921. Cefn Caer – Roman fort in An Inventory of the Ancient Monuments in Wales and Monmouthshire VI. County of Merioneth RCAHM
Bowen, E.G. and Gresham, C.A. 1967. History of Merioneth. Volume 1: From the earliest times to the Age of the Native Princes. The Merioneth Historical and Record Society
Davies, J. 2007 (third edition). A History of Wales. Penguin
Davies, J. and Lynch, F. 2000. The Late Bronze and Iron Age. In (eds.) Lynch, F., Aldhouse-Green, S. and Davies, J.L. Prehistoric Wales. Sutton Publishing
Gwyn, D and Davidson, A. 2007. Ports and Harbours of Gwynedd: Aberdyfi. A Threat Related Assessment. GAT Project No. 1824. Report No. 671.1. April,2007. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust
Hopewell, D. 2001. Roman Fort Environs G1632, Report 416. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust 2001. http://www.walesher1974.org/her/groups/GAT/media/GAT_Reports/GATreport_416_compressed.pdf
Hopewell, D. 2003. Roman Fort Environs 2002/2003, G1632, Report number 479. Gwynedd Archaeological Reports. http://www.walesher1974.org/her/groups/GAT/media/GAT_Reports/GATreport_479_compressed.pdf
Hopewll, D. 2007. Roman Fort Environs. Geophysical Survey at Trawscoed Roman Fort and Erglodd Fortlet. G1827(2). Report number: 667. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust. http://www.dyfedarchaeology.org.uk/projects/07romanergloddgeophys.pdf
Irvine, H.C. 1957. Bulletin of the Board of Celtic Studies Volume XVII part 2, (p.124-131)
Coflein entry on Cefn Caer:
https://coflein.gov.uk/en/site/300159/details/cefn-caer-roman-fortpennal-roman-fort
Coflein entry on Brithdir fortlet:
https://coflein.gov.uk/en/site/95480/details/brithdir-roman-site





A great piece on Cefn Caer. I grew up in Tywyn and it was a place I always meant to visit, but never did. One day! You mentioned Iron Age forts in the area, and yes your right there aren’t many in comparison with further south along the coast or to the North East along the present border with England. I assume you’ve visited the fort on a Craig Aderyn, always worth a walk up there. There’s a couple on Beacon Hill as well, but they are difficult to discern on the ground. The most obvious one is Castell y Gaer just south of Llwyngwril.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hi Paul, good to hear from you. I have been really enjoying your blog. There isn’t a lot to see when you get there! Although I do want to see the farm, which is open to the public by appointment. I was going to do a post on Tomen Mur but will just post a link to your post instead, although having seen your excellent photos I do want to visit. The Iron Age hillforts of the area are an upcoming project. Thanks very much for the pointers – I hadn’t got to the stage of finding out what they are called and where they are located, so that is a very useful start! Hillforts are always a bit of a pain to photograph, even with a really wide angle lens, but hopefully Coflein will have some reasonable aerial shots.
LikeLiked by 2 people
It’s off the back road to Llugwy?
LikeLiked by 1 person
“Another Meirionnydd fort at Brithdir, 3 miles east of Dolgellau, was found in the early 1960s and is clearly connected by a contemporary road to Cefn Caer at Pennal……Research by Hugh Toller, for example, is thought to have uncovered a number of previously unknown sections of the RRX96 road between Pennal and Brithdir”
I am interested in the route of this road – can you advise where more information can be found ?
LikeLike
Hi Richard. I’ll dig out the document that mentioned Hugh Toller’s research sometime over the weekend. The mapping of Roman roads in this area seems to have been quite a significant challenge.
LikeLike
Richard, I haven’t had chance to look for the document I used, but I know that it just made a passing comment. This is almost certainly what it was based on. If you don’t have access to JSTOR let me know – I may be able to get access to it. https://www.jstor.org/stable/526687?seq=1.
LikeLike
Andie, thanks for the link – I can only access the preview, which mentions the Roman road SE of Brithdir being cut by the later turnpike. Any other mentions of the Brithdir-Pennal road would be of interest.
LikeLike
Leave it with me – I’ll be back in touch next week.
LikeLike
Hi. I accessed the document but it deals exclusively with post-Medieval turnpikes. It cites an earlier work by Rigg and Toller (A Roman road from the Long Mountain to Dolgellau and some branches, Britannia Vol. 30 (1999), pp. 299-301 ) but in the turnpike paper Toller says that nearly all the roads that were described as Roman in that earlier paper are now thought to be post-Medieval. The only other information I have been able to find on that particular stretch of the road network are as follows:
https://www.coflein.gov.uk/en/site/286687/details/part-of-roman-road-brithdir-cefn-caer-pennal
https://www.snowdonia.gov.wales/addysg-education/snowdonia-from-the-air/the-roman-occupation/lines-of-communication
http://www.heneb.co.uk/cadwprojs/cadwreview2007/romanroads07.html
LikeLike
“Another Meirionnydd fort at Brithdir, 3 miles east of Dolgellau, was found in the early 1960s and is clearly connected by a contemporary road to Cefn Caer at Pennal….. Research by Hugh Toller, for example, is thought to have uncovered a number of previously unknown sections of the RRX96 road between Pennal and Brithdir.”
I am interested in the route of this road – can you tell me where I can find more information ?
LikeLike